North Korea Latest News,Why North Korea must develop nuclear weapons?
First of all,Let's take a look at the North Korean nation first.
DPRK (Democratic People's Republic of Korea):
Democratic People's Republic of Korea (Korean: ???????????, English: Democratic arranges ' s Republic of Korea, abbreviation: DPRK), abbreviation North Korea, North Korea, North Korea. is located in East Asia Korean Peninsula north of the socialist country, the ruling party is the Korean Labor Party. South and South Korea with 38 lines to the Han Fei military zone, the north and the People's Republic of China and Russia border, west of the Bohai Sea, and Shandong Peninsula across the sea, east of the Japanese sea. Capital of Pyongyang.
The socialist regime was established on September 9, 1948 after the Second World War, with an area of 122762 square kilometres and a population of 25.155 million (2015). The Korean national/Korean nationality is a unitary nation, the universal Korean language. In military, the emphasis on the first Army thought as the guidance to strengthen national strength. North Korea currently has about 1.2 million soldiers and is the world's largest armed forces in the five countries.
North Korea announced 1958 completed the socialist Transformation of urban and rural production relations, and established a socialist economic system. Socialist Industrialization was proclaimed in 1970. May 1975, became a full member of the "Group of 77" and formally joined the Non-Aligned Movement in August. September 17, 1991 joined the United Nations with South Korea. July 2000, joined the ASEAN Regional Forum (ARF). Diplomatic relations were established with 163 countries (including the European Union).
North Korea was led by the first leader, Kim Il-sung, to dominate the national policy by the DPRK Labor Party. Its political and economic system is dominated by the First Army politics, and it is the country that insists on socialism. North Korea pursues an "independent, peaceful and friendly" foreign policy, advocating the development of foreign relations in accordance with the principles of full equality, autonomy, mutual respect, non-interference in each other's internal affairs and mutual benefit. November 20, 2017, the United States Government announced that the DPRK was again included in the list of states supporting terrorism
Why North Korea must develop nuclear weapons?
The two Koreas resumed talks recently because of the Winter Olympics. To promote peaceful reunification of the peninsula, both sides have unleashed great goodwill. But the North Korean nuclear issue is still an important issue to be faced by both sides. It is impossible for North Korea to give up its nuclear weapons to the South, which is shivering in its hands. Behind the North Korean nuclear issue, it is not only the game between the two sides, but also the survival of this special country.

The Korean peninsula the big news on the beginning of year
January 9, the two Koreas in Panmunjom on the Korean side of the "Peace House" to discuss the DPRK to participate in the Pingchang Winter Olympics related matters. South Korean President Moon, who has always advocated balanced diplomacy, has unleashed great goodwill on North Korea, even posing as a departure from the United States to ban the blockade.


South Korean delegation head Zhao (left)
Li Shanquan (right), head of delegation of the DPRK side
The looming nuclear issue at the end of last year, and the reunification of the peninsula behind it, seem to have a sudden thaw in the possibility of moving forward.
Today's article will take you to look at, behind these changes, North Korea actually experienced what kind of suffering? What has been the development of North Korea's nuclear weapons to make the peninsula situation so changeable?

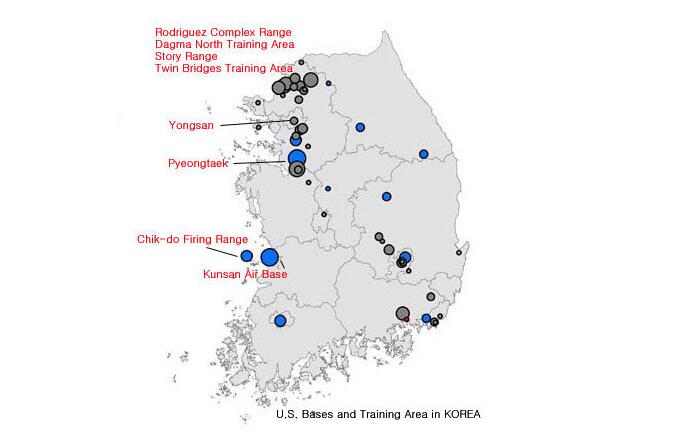
North Korea's obsession with nuclear weapons began in the Korean War, and it was precisely the nuclear threat that originated in the United States. In the Korean War, the United States several times threatened to use nuclear weapons against North Korea, although it was not implemented. But the United States in 1958 or South Korea to decorate about 2,600 pieces of nuclear weapons, and since the war has not been withdrawn from the Korean peninsula.
U.S. military base and training zone in South Korea

Therefore, compared with the first nuclear test in 2006, North Korea decided to start nuclear technology research as early as the 1950s after the Korean War, and in the middle of 60, with the help of the former Soviet Union, founded the Atomic energy research base in Yongbyon.
Yongbyon 5MW (MW) reactor

For North Korea, the support of the former Soviet Union and China seems less plausible than the U.S. 's "good sense" for its ally, South Korea, against the backdrop of the Cold War. Both have made a security pledge to North Korea, but their pledges do not include nuclear protection or the presence of troops in the north.

In view of their own and alliance relations and the strength of the United States alliance between the Gap, but also consider the door at the mouth of the nuclear threat, North Korea into the country's security dilemma. Under such a dilemma, North Korea's most basic interests are self-preservation and tend to develop nuclear technology.
Against this backdrop, North Korea purchased a 800-kilowatt nuclear reactor from the former Soviet Union in the 70 's, and the Yongbyon nuclear technology study was therefore a qualitative improvement, and in 1987 it successfully extracted the plutonium that could be used to make nuclear weapons.
Plutonium
Silvery-white, in the air of the lost gloss for the dark grey
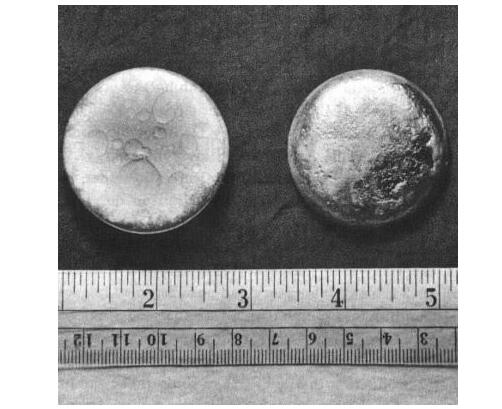

The atomic bomb, which was invested in Japan's Nagasaki in 1945, contains a plutonium nucleus

However, the short-lived. 1990, the U.S. Department of Defense and intelligence agencies through satellite photos and the relevant information to determine that North Korea, about 90 kilometers north of Pyongyang, an additional nuclear reactor in the Yongbyon area of the nuclear weapons can be extracted from the production of plutonium. After uniting international support, the U.S. government publicly denounced North Korea's nuclear weapons development in September 1991, claiming it had to inspect North Korea's nuclear facilities.
Time is long, it's bigger.
The Korean attitude of the 90 's was much more moderate than it is today. North Korea at the time did not object to a nuclear inspection, but asked for the same inspection of South Korea and the withdrawal of the U.S. nuclear weapons deployed. In a repeated conflict with the United States, North Korea has been trying to resolve the issue through consultations, for which it agreed to the International Atomic Energy Agency for a number of local inspections to show the sincerity of the DPRK, hoping that the United States can withdraw and aid North Korea

But America's stance is tough, and it can only take into account North Korea's demands by fully inspecting its entire territory and ensuring a nuclear-free one.
The standoff between North Korea and the United States is precisely the embodiment of the predicament of national security in reality: Both sides logically make decisions that are reasonable to their own national interests, but the two sides ' stance towards the DPRK nuclear issue has become doomed.
US experts check the Yongbyon nuclear research station

Thankfully, the North Korean nuclear crisis has not escalated again, and the two sides have at least reached a consensus on communication.
Transition: From Kim Jong Il to Kim Jong Un
During Kim Jong Il's reign from 1994 to 2012, North Korea's nuclear weapons developed relatively slowly. The nuclear strategy of the Kim Jong Il era is also relatively confusing. For outsiders, the true intentions of North Korea are hard to grasp.
On the face of it, Kim Jong-il implemented a "nuclear abandonment" policy, namely, the development of nuclear weapons to obtain the bargaining space, the real goal is not to develop nuclear weapons. So for a long time, the international community generally agreed that North Korea's nuclear issue was merely a means of normalizing relations with the United States.

North Korea announced in 2002 that it wanted to develop nuclear weapons and hoped to hold talks with the United States, but the United States refused bilateral talks. Finally reached the six-party talks, China, South Korea, the United States, Russia, Japan and North Korea to jointly negotiate the resolution of the nuclear issue of the peninsula.
The DPRK nuclear issue is a regional issue
But because of the big players involved,
is already a global problem.
In the six negotiations between 2003 and 2007, North Korea has generally been a positive gesture to push the peninsula to nuclear. Of course, this period, also inevitable twists and turns. Among them, North Korea on October 9, 2006 in the Jizhou County of Xian Jing River in the area of the first nuclear test, the magnitude 4.2, equivalent to 800 tons.
Because the equivalent of less than thousand tons, the United States at first did not buy, that is North Korea's bluff, refused to recognize this is a nuclear test. The international mainstream also believes that North Korea's nuclear test is only a response to U.S. sanctions against the DPRK, in order to increase the weight of the DPRK nuclear talks.
Although the six-party talks are the only multilateral political settlement mechanism to resolve the DPRK nuclear issue, it is noteworthy that the six-party talks only set the highest goal of "denuclearization of the Korean peninsula", but there is no written form for the United States, China, Japan and Russia to jointly prevent North Korea from conducting nuclear tests. In other words, the six-party talks, which lasted 5 years, did not form an effective binding mechanism for North Korea to conduct nuclear tests.
The more participants, the longer the negotiations.

At the same time, the external environment facing North Korea has changed markedly.
First, Korea's diplomatic attitude towards the DPRK has changed dramatically.
Since the 1998, the two governments, Kim Dae-jung and Roh Moo-hyun, have adopted a moderate "sunshine policy" on North Korea, which holds three basic principles on North Korea: First, there is no intention to annex, two, no military provocation, third, the pursuit of peaceful coexistence.
In February 2008, however, the Lee Myung-bak government abandoned the former two governments to the DPRK policy, instead of implementing the "Three principles of the DPRK policy", namely "nuclear-free, open, 3000", the core content is that the DPRK completely abandon the nuclear, foreign fully open, under the premise of Korea to help North Korea 10 years per capita income of 3000 U.S. dollars. Such a tough attitude worsened relations between the Koreas.

Second, the U.S. government due to internal and external difficulties, the North Korean issue of concern and the amount of aid to the DPRK has been declining. Since the first North Korean nuclear crisis, North Korea has received less aid and benefits through its "blackmail" approach and has not been a security commitment to the United States.
In this context, North Korea issued a statement, said that even if there is no normalization of relations with the United States can survive, but without the nuclear deterrent force, it cannot survive, this is the reality of the Korean peninsula. And then announced the withdrawal of the six-party talks.
The sea sails on dad.

On May 25, 2009, North Korea carried out a larger second nuclear test in the underground facility of the Jizhou County in the south of the Salt mirror, with a magnitude of 4.5 to 5.3 and an inferred equivalent of 12,000 tonnes.

The US and South Korea have repeatedly responded with frequent military exercises and sanctions, and the relationship seems to have lost its balance.
With the sudden death of Kim Jong-il in 2011, Kim Jong-un took over the North Korean regime and accelerated the nuclear move. Facing the internal and internal problems of North Korea, Kim Jong-un chose to start with the nuclear issue, openly expounded North Korea's "nuclear" policy, and for the first time to write a nuclear-related to the Constitution. "The path of economic construction and nuclear force development" demonstrates North Korea's determination to move forward on the path of nuclear weapons and nuclear arms.

Through this move, Kim Jong-un consolidated the legitimacy of the regime and formed a strategic deterrent to the outside world.
So far, North Korea's nuclear weapons have entered a period of rapid development.
The American Compromise
February 12, 2013, North Korea in the Jizhou County, south of the salt mirror nuclear test site carried out a third underground nuclear test, estimated equivalent to 6000 to 7000 tons of TNT explosive.
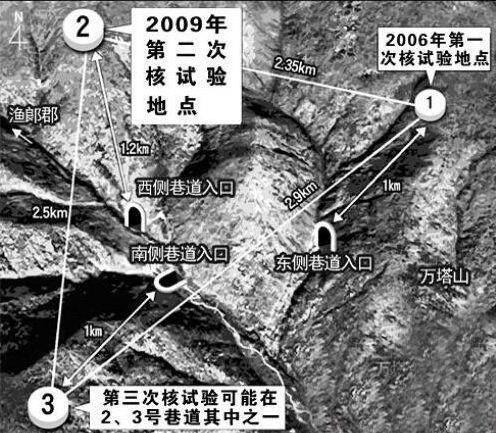
January 6, 2016, North Korea in the Fung Creek nuclear test Site successfully conducted a hydrogen bomb test, equivalent to about 11.3 thousand tons. Because of the small explosion equivalent, it is generally not considered the test is a hydrogen bomb test. The United States has also claimed that they believe North Korea tested the hydrogen bomb components in the test, but failed.
January 6
Residents of Pyongyang gather in front of the station's square screen
Watch a report on the success of the hydrogen bomb test

Even so, the test from a nuclear bomb to a hydrogen bomb has provoked a strong reaction from South Korea. South Korea has adopted a series of measures to deal with North Korea, the most notable of which is the introduction of "strategic weapons", the resumption of THAAD ("Sade" system, the terminal High-altitude Regional defense system).
Think carefully, in 2016, North Korea's nuclear test, compared with the past, in fact, a more emphasis on China's strategic pressure. The reason is that park after the stage, and even participated in the 15-year 9 3 parade, China and South Korea into the honeymoon period, which is clearly not good news for North Korea. The nuclear test forced South Korea to restart Sade, will be able to cool Sino-rok Relations, let Northeast Asia's strategic structure reshuffle.
September 9, 2016, North Korea in the North Fung Creek Nuclear test site conducted the fifth nuclear test, the magnitude of 5. 3. According to South Korean military sources, the nuclear test's explosion equivalent or reached 10,000 tons of TNT equivalent. North Korea's nuclear test on its national day, September 9, is not only a domestic celebration, the stability of the Korean public, but also the external pressure to show North Korea's nuclear power.
Judging by the scale of the first five nuclear tests, North Korea's nuclear power is indeed growing. But North Korea does not have the capacity to carry out a nuclear strike because it has an important flaw in technology such as miniaturization and ballistic missiles, and cannot be called a "de facto nuclear State".

September 3, 2017, North Korea conducted a second hydrogen bomb test, the magnitude of 6.3, the equivalent of conservative estimates for 10~20 million. The nuclear explosion has reached 3 to 7.8 times times the power of the US's "Fat Man" in Nagasaki, the largest ever in the history of North Korea.
The day is the BRICS conference held in China, the DPRK "nuclear celebration" that the DPRK nuclear issue has been out of China can affect the scope. In a political sense, the level of the Korean nuclear crisis has risen again. This angered China, the 19 period of the United States and South Korea's joint military exercises against the DPRK, China has not issued an official statement is the most direct embodiment.

From September to December, America's attitude towards the DPRK was too strong. But what exactly is the negotiable message that the Trump government suddenly released in late December?
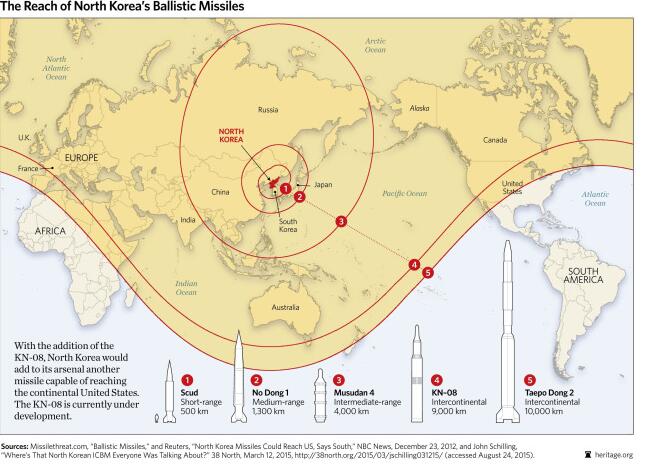
The direct factor is also simple, with North Korea having a nuclear strike capability. November 29, North Korea in the flat Annandaoping city towards the eastern waters of the peninsula Test-fired long-range ballistic missile, flying altitude of 4500 km, range of about 960 km.
North Korea's "Mars 15" could already be an intercontinental ballistic missile with a range of more than 10000 kilometres and a 700-800 kg ability to throw, which means that most of Asia and the United States will be covered by North Korean missiles.
Powerful
The new year, the peninsula situation is still uncertain, but perhaps for North Korea, the nuclear this step is the right way. And it is probably because of the nuclear, the DPRK has a peaceful solution to the issue of the peninsula's favorable bargaining chip.

posted by Topscom News from world news of usa,on Janu 28,2018


